Introduction
Ever wondered how those velvety textures on your favorite items are made? Electrostatic flocking machine is the magic behind that smooth, luxurious finish on a variety of products. Whether it’s the soft interior of a jewelry box or the rich feel of automotive interiors, flocking adds that special touch.
This guide will take you through the process of using an electrostatic flocking machine. We’ll explain the science behind it and offer step-by-step instructions for flawless results. By the end of this post, you’ll know how to set up and operate a flocking machine, understand the electrostatic principles at play, and troubleshoot common issues. Get ready to master the art of flocking!

What is Electrostatic Flocking?
Understanding Flocking: The Basics
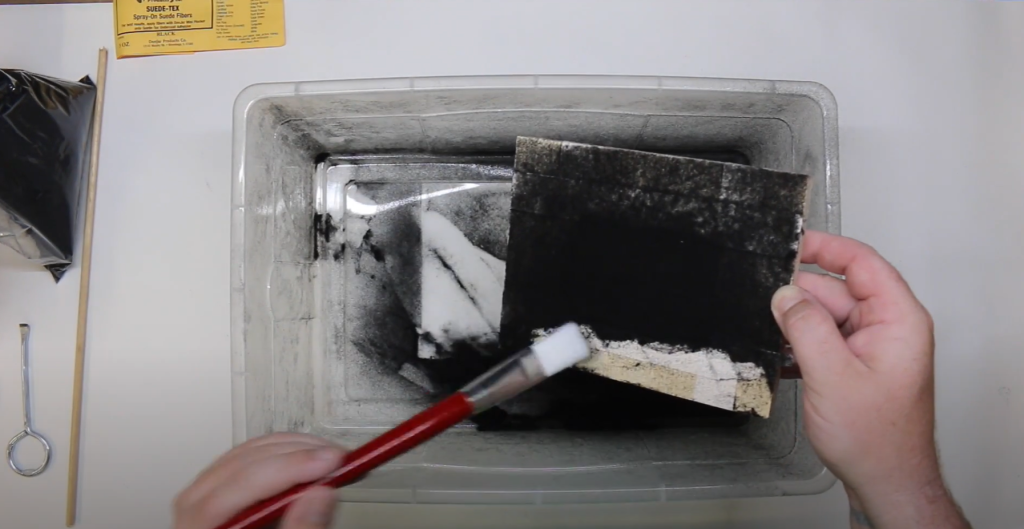
Ever noticed the soft, velvety texture on certain products and wondered how they achieve that look? That’s where electrostatic flocking comes in. It’s a process that involves applying tiny fiber particles onto a surface to create a textured finish. The magic happens when these fibers are given an electrostatic charge, making them stand upright as they adhere to the adhesive-coated surface. This results in a uniform, luxurious texture that’s both appealing and functional.
Common Applications of Electrostatic Flocking
Electrostatic flocking isn’t just for high-end products; it’s used in a variety of everyday items. Here are some common applications:
- Textiles: Flocking adds a soft, tactile quality to clothing and accessories, making them more comfortable and stylish.
- Automotive Interiors: Car manufacturers use flocking for dashboards, glove compartments, and other interior components to provide a smooth, premium feel.
- Arts and Crafts: Flocking is popular in DIY projects, from greeting cards to model-making, giving them a professional and polished look.
- Packaging: Jewelry boxes, cosmetic cases, and other packaging often feature flocking for an upscale appearance.
🔔You can learn everything there is to know about electrostatic flocking in this blog post.
The Science Behind Electrostatic Flocking
How Electrostatics Works in Flocking
Electrostatic flocking might sound complicated, but it’s based on straightforward principles of physics. Let’s break it down:
- Electrostatic Charge: The heart of flocking lies in electrostatics, the branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest. In the flocking process, the flock fibers are given an electrostatic charge using a flocking machine. This charge makes the fibers behave like tiny magnets.
- Adhesive Application: Before applying the fibers, the target surface is coated with a specialized adhesive. This adhesive acts as a glue that holds the fibers in place. The adhesive needs to be tacky enough to attract and hold the fibers upright as they land.
- Fiber Attraction: When the charged fibers are sprayed onto the adhesive-coated surface, the opposite charges attract. This attraction ensures that the fibers stand upright, creating a uniform, velvety finish. The electrostatic charge makes sure the fibers are evenly distributed, avoiding clumping and uneven patches.
Key Components of Electrostatic Flocking
Understanding the main components involved in the flocking process helps in grasping how it all comes together:
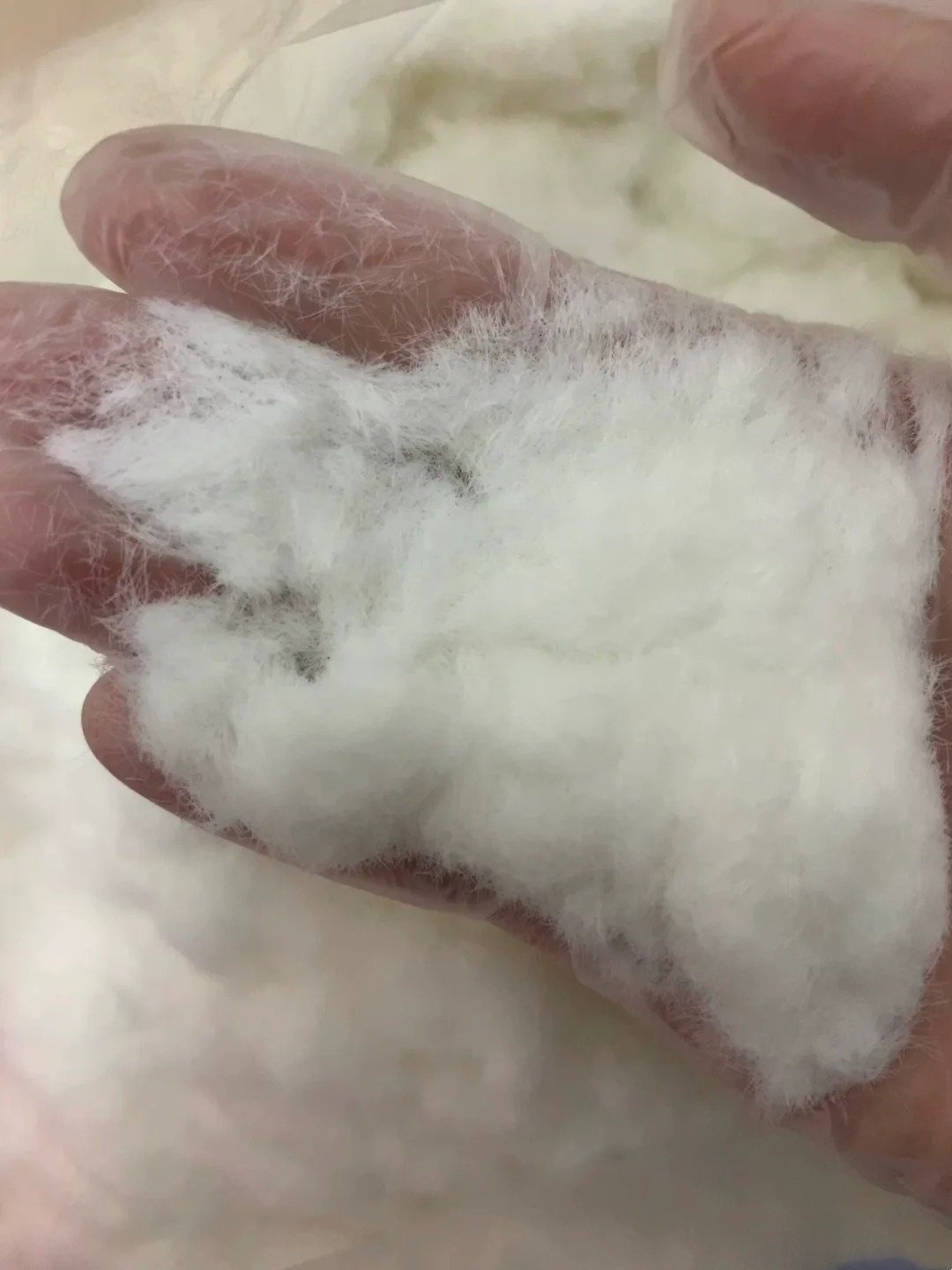
- Flock Fibers: These are minuscule particles, often made from materials like nylon, rayon, or polyester. The choice of material affects the final texture and durability of the flocked surface. The fibers can vary in length and thickness, which also influences the finish.
- Adhesive: The adhesive is crucial for the flocking process. It must be compatible with the substrate (the material being flocked) and the fibers. The adhesive’s properties, such as drying time and tackiness, play a significant role in the quality of the finished product.
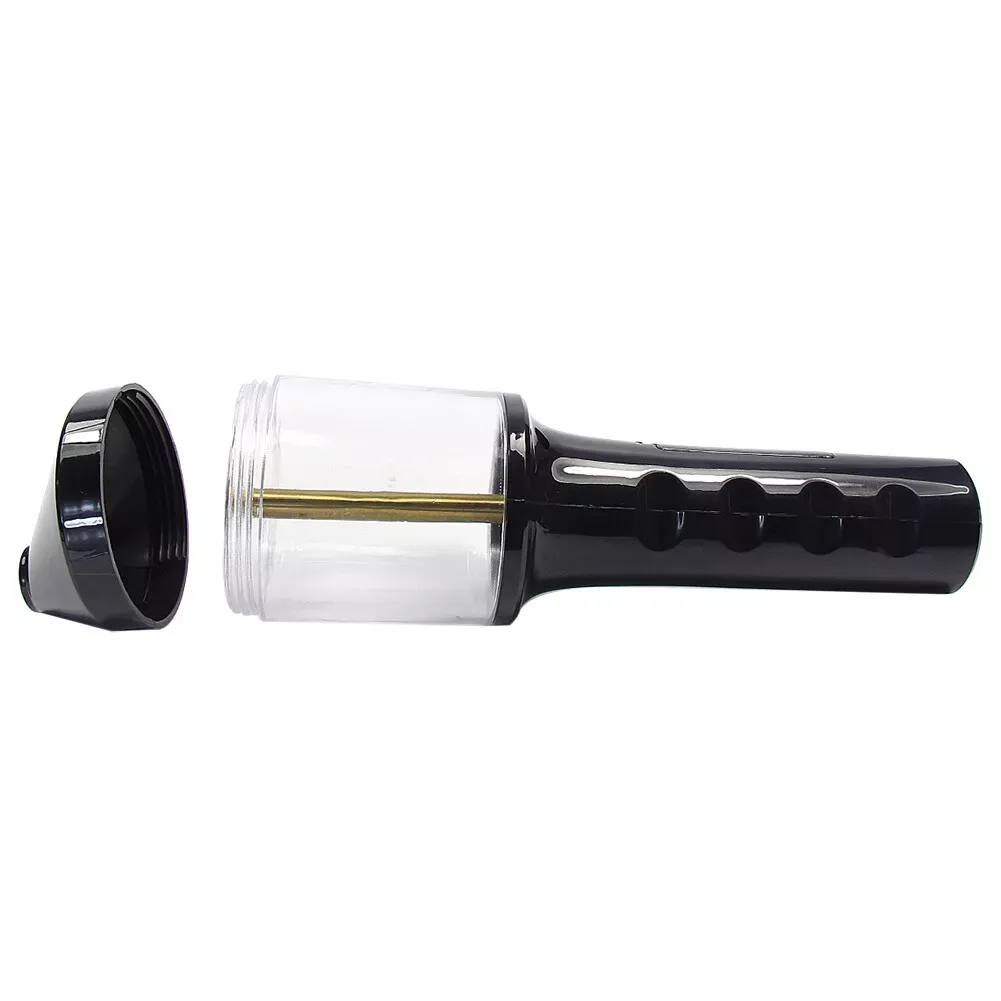
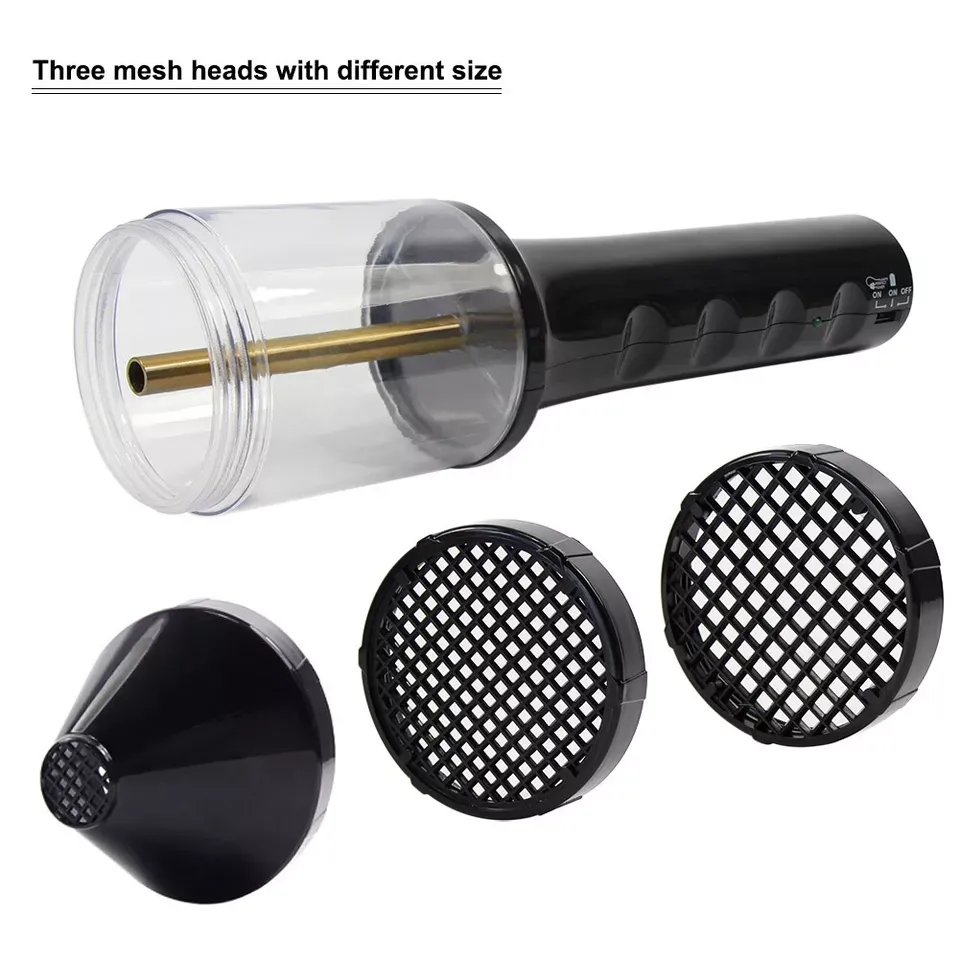
- Flocking Machine: This is the equipment that charges and applies the fibers. The machine consists of several parts, including a power supply to generate the electrostatic charge, a flocking gun to spray the fibers, and a grounding system to ensure safety and efficiency.
Benefits of Electrostatic Flocking
Using electrostatic flocking offers several advantages:
- Uniform Coverage: The electrostatic charge ensures fibers are evenly distributed, creating a smooth, consistent finish without clumps or bare spots.
- Durability: Flocked surfaces are resistant to wear and tear, maintaining their appearance over time even with regular use.
- Enhanced Aesthetics: The velvety texture adds a touch of luxury and sophistication to any product, making it visually appealing and pleasant to touch.
Electrostatic flocking combines scientific principles with practical application to produce high-quality, durable, and aesthetically pleasing finishes on a variety of products. Whether you’re enhancing textiles, automotive interiors, or crafting projects, understanding and applying these techniques can help you achieve professional results.
Inside an Electrostatic Flocking Machine: Key Components and Safety Tips
The Main Parts of an Electrostatic Flocking Machine
Understanding the different parts of an electrostatic flocking machine is essential to using it effectively. Let’s break down the key components and their functions:
Power Supply and Electrostatic Generator
- Power Supply: This is the backbone of the machine, providing the necessary electricity to generate an electrostatic charge. It’s crucial for converting standard electrical power into the high voltage needed for flocking.
- Electrostatic Generator: This component generates the electrostatic charge that will be transferred to the flock fibers. It creates a strong, consistent charge to ensure the fibers stand up and adhere properly to the adhesive-coated surface.
Flocking Gun
- Flocking Gun: Think of this as the tool that sprays fibers onto your surface. The flocking gun charges the fibers and ensures even distribution. Designed for easy handling, it allows for precise control over the application process. Adjust the gun’s settings for different types of fibers and applications.
Grounding System
- Grounding System: Safety first! The grounding system ensures that any excess electrical charge is safely dissipated, preventing shocks and ensuring a stable application environment. Proper grounding is crucial for both the safety of the user and the efficiency of the flocking process.
Adhesive Application System
- Adhesive Application: Before you can flock, you need a way to apply adhesive to your surface. Use brushes, rollers, or spray systems to apply the adhesive, depending on the object’s size and shape. Apply the adhesive evenly to ensure the fibers stick properly and the final texture remains smooth and uniform.
Safety Features of an Electrostatic Flocking Machine
Using an electrostatic flocking machine involves high voltage, so safety is paramount. Here are some essential safety features and tips:
Grounding and Electrical Safety
- Grounding: Always ensure that the machine is properly grounded. This prevents the build-up of static electricity that could cause shocks or interfere with the flocking process. Check the grounding connections regularly to ensure they’re secure and functioning correctly.
- Electrical Safety: Use the machine in a dry environment to avoid the risk of electrical shorts or shocks. Make sure all electrical components are in good condition, and don’t operate the machine if any wires or connections are damaged.
Protective Gear and Precautions
- Protective Gear: Wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves, safety goggles, and a dust mask. This gear protects you from the adhesive, fibers, and any potential static discharge.
- Work Area: Keep your work area clean and free of unnecessary items. This reduces the risk of accidents and makes it easier to move around while working with the machine.
- Ventilation: Ensure good ventilation in your workspace to avoid inhaling adhesive fumes or fiber particles. Use fans or work in a well-ventilated area to keep air circulating.
By understanding and respecting these components and safety measures, you can ensure that your electrostatic flocking projects are not only successful but also safe. Proper setup and handling of your flocking machine will lead to better results and a more enjoyable flocking experience.
Getting Started with Your Electrostatic Flocking Machine
Setting Up Your Workspace
Before diving into flocking, you need to create the right environment for the job. A well-prepared workspace not only makes the process smoother but also ensures your safety.
Ideal Work Environment
- Clean and Dry: Your workspace should be free from dust and moisture. Dust can interfere with the adhesive, and moisture can affect the electrostatic charge. Make sure to clean the area thoroughly before starting.
- Well-Lit: Good lighting helps you see the details better, ensuring you don’t miss any spots while applying adhesive or flock fibers.
- Ventilated: Proper ventilation is crucial to avoid inhaling adhesive fumes or fiber particles. Use fans or open windows to keep the air circulating.
Safety Precautions and Equipment
- Gloves and Goggles: Wear protective gloves to keep your hands safe from adhesive and fibers. Safety goggles protect your eyes from any stray fibers or adhesive splashes.
- Dust Mask: A dust mask can help prevent you from inhaling tiny fiber particles, which can be harmful over time.
- Grounding Wrist Strap: Using a grounding wrist strap can help prevent static shock and ensure your safety when working with the electrostatic flocking machine.
Setting Up the Electrostatic Flocking Machine
Once your workspace is ready, it’s time to set up your flocking machine. Follow these steps for a smooth setup:
Unboxing and Assembling the Machine
- Unbox Carefully: Remove all parts from the box, making sure you have everything you need. Refer to the instruction manual for a checklist of components.
- Assemble the Machine: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to assemble your electrostatic flocking machine. This usually involves attaching the flocking gun, connecting hoses, and securing any other parts.
Connecting the Power Supply and Grounding System
- Power Supply: Plug the power supply into a reliable electrical outlet. Ensure that the outlet can handle the voltage required by your machine.
- Grounding System: Connect the grounding system as instructed. Proper grounding is crucial for safety and effective flocking. Check all connections to ensure they are secure.
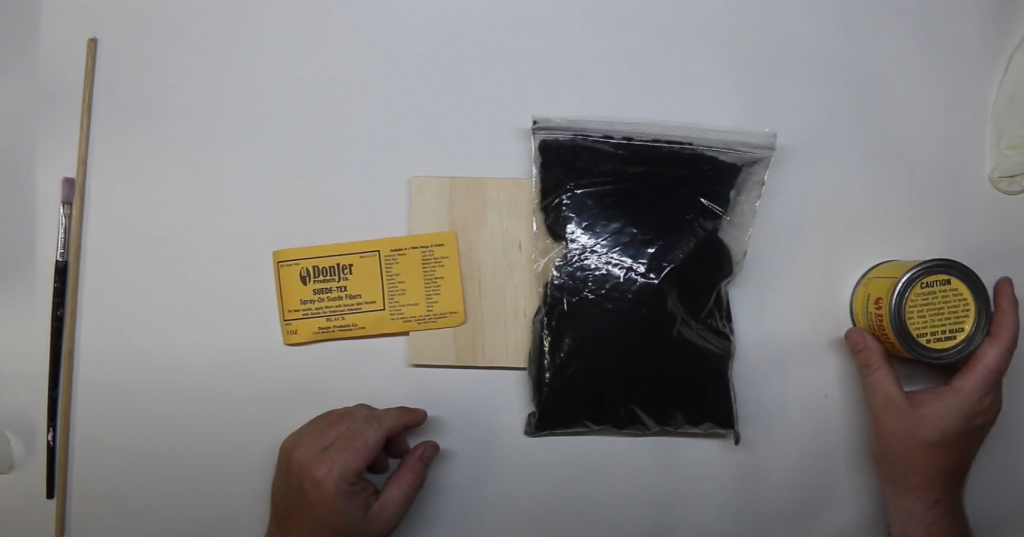
Preparing the Flock Fibers and Adhesive
- Select Your Fibers: Choose the type of flock fibers suitable for your project. Make sure they are clean and dry before use.
- Prepare the Adhesive: Depending on the adhesive type, you may need to mix it or prepare it in another way. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the best results.
- Load the Flocking Gun: Fill the flocking gun with the prepared flock fibers. Ensure the gun is securely attached to the machine and ready for use.
Final Checks and Tips
- Test Run: Before starting on your actual project, do a test run on a scrap piece. This helps you get a feel for the machine and make any necessary adjustments.
- Adjust Settings: Check the machine settings and adjust them according to the type of fibers and adhesive you are using. This ensures optimal performance.
- Stay Organized: Keep all tools and materials within reach. Having everything organized will make the process smoother and more efficient.
By following these steps, you’ll be well-prepared to use your electrostatic flocking machine. A well-organized workspace and a properly set up machines are the keys to achieving professional and consistent results. Happy flocking!
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the Electrostatic Flocking Machine
Ready to start flocking? Here’s a detailed guide to help you use your electrostatic flocking machine like a pro.
Preparing the Surface
Before you begin flocking, you need to prepare your surface to ensure the adhesive and fibers adhere properly.
Cleaning and Priming the Surface
- Clean Thoroughly: Remove any dirt, dust, or grease from the surface. Use a mild detergent and water for cleaning, and make sure the surface is completely dry before proceeding.
- Prime if Necessary: If you’re working with a surface that doesn’t bond well with adhesive, apply a primer. This will help the adhesive stick better and ensure a smooth finish.
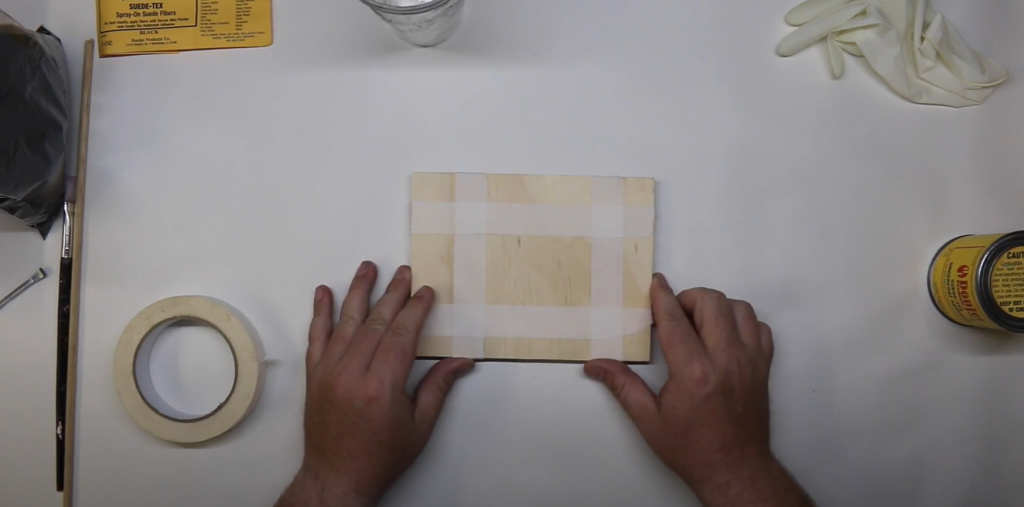
Applying the Adhesive Evenly
- Choose the Right Adhesive: Make sure you’re using an adhesive that is compatible with both your surface and flock fibers.
- Apply Evenly: Use a brush, roller, or spray gun to apply the adhesive in a thin, even layer. Avoid puddles or uneven spots, as these will affect the final texture.
Applying the Flock Fibers
Now that your surface is ready, it’s time to use the electrostatic flocking machine to apply the fibers.
Adjusting Machine Settings
- Set the Voltage: Adjust the machine to the recommended voltage for your flock fibers. This information is usually provided by the manufacturer.
- Determine the Distance: Position the flocking gun at the correct distance from the surface, typically around 8-12 inches. This ensures the fibers are properly charged and will stick upright.
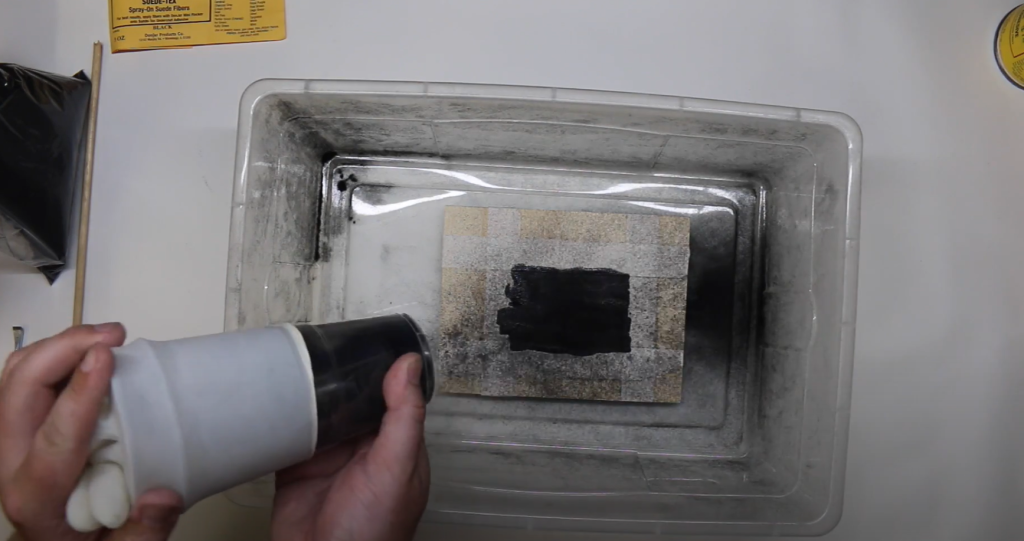
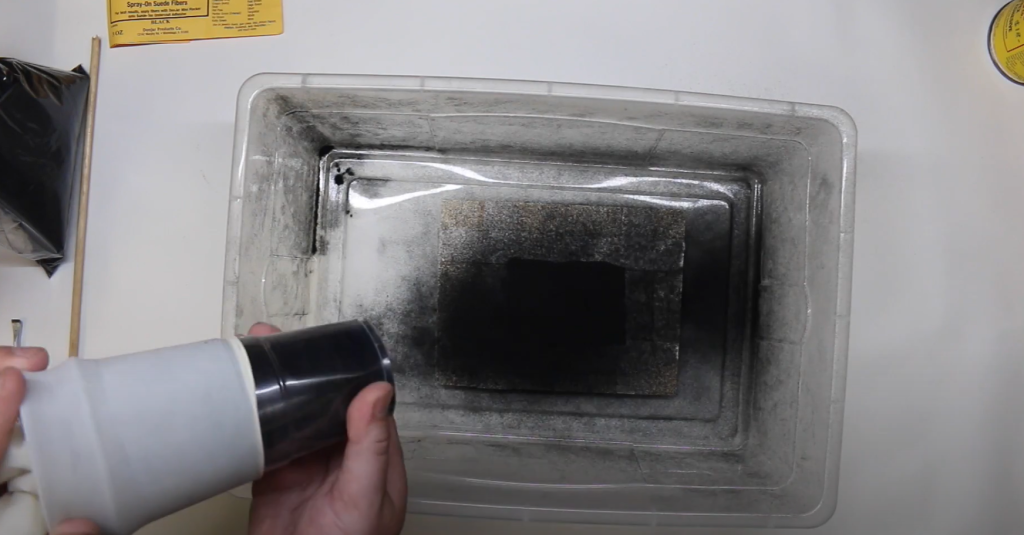
Using the Flocking Gun for Even Coverage
- Even Spraying: Hold the flocking gun steady and move it evenly across the surface. Overlapping your passes slightly helps ensure complete coverage.
- Adjust as Needed: If you notice any areas with too many or too few fibers, adjust your technique or settings to achieve an even distribution.
Techniques for Different Surfaces and Textures
- Flat Surfaces: Move the gun in straight, even lines to cover flat surfaces uniformly.
- Curved or Textured Surfaces: For uneven surfaces, use a circular motion to ensure fibers reach all areas. Adjust the distance and angle of the gun as needed.
Curing and Finishing
After the fibers are applied, final steps ensure the adhesive cures properly and the finish looks professional.
Allowing the Adhesive to Cure
- Drying Time: Let the adhesive cure according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This usually takes several hours. Ensure the environment is free from dust during this period.
- Check the Surface: After the adhesive has cured, inspect the surface to ensure that all the fibers are securely attached.
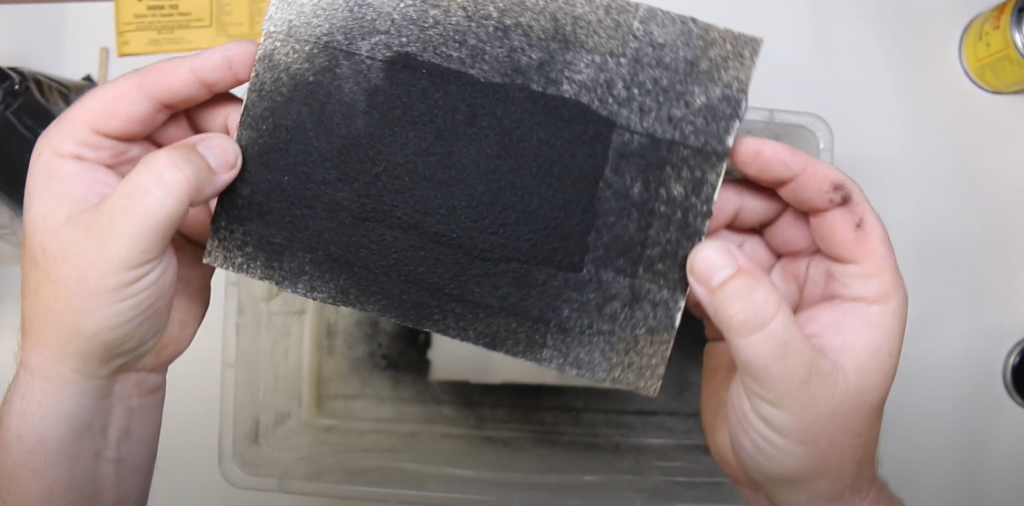
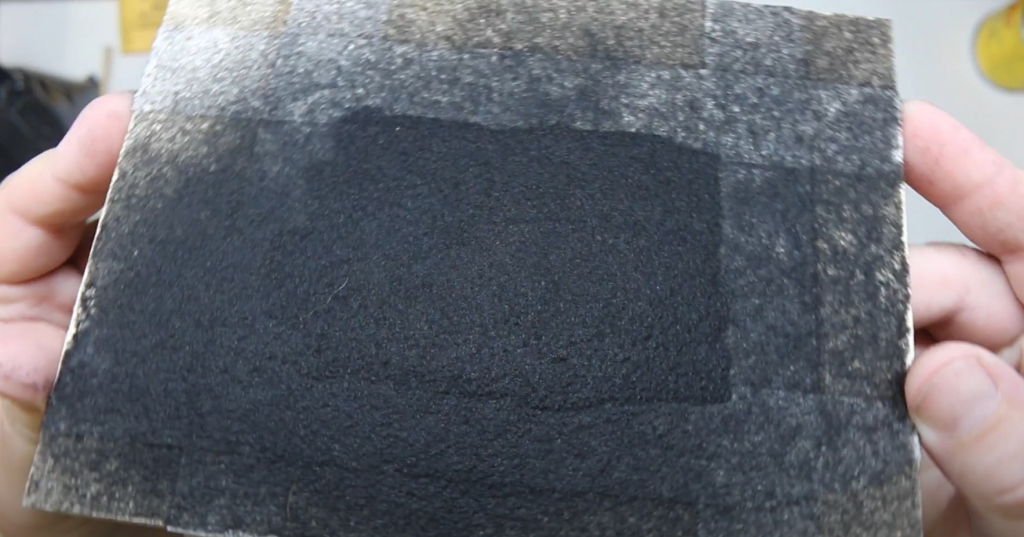
Removing Excess Fibers and Inspecting the Finish
- Remove Excess Fibers: Gently brush or vacuum away any loose fibers that don’t stick. Be careful not to disturb the adhered fibers.
- Inspect the Finish: Look for any uneven areas or spots that need touch-ups. Use the flocking gun to add more fibers if necessary.
Tips for Achieving a Professional Look
- Consistent Adhesive Application: Ensuring an even layer of adhesive is key to a uniform flocked finish.
- Proper Lighting: Work in a well-lit area to easily spot and correct any imperfections.
- Practice Makes Perfect: Do a few test runs on scrap pieces to get a feel for the process before working on your final project.
By following this step-by-step guide, you’ll be able to use your electrostatic flocking machine effectively and achieve a professional, smooth finish every time. Happy flocking!
Conclusion
Mastering the use of an electrostatic flocking machine opens up a world of creative possibilities. With the right preparation, technique, and safety measures, you can achieve stunning, professional-quality results. Now that you know the ins and outs of flocking, it’s time to start your own projects.
Get your materials ready, set up your machine, and let your creativity shine with beautifully flocked surfaces! Happy flocking!